Every year in July, we recognize UV Safety Awareness Month, bringing attention to the risks of overexposing yourself to UV rays. Skin cancer is the most significant danger of UV overexposure, so this article provides correlating information and tips to mitigate your risks.
What Is Skin Cancer?
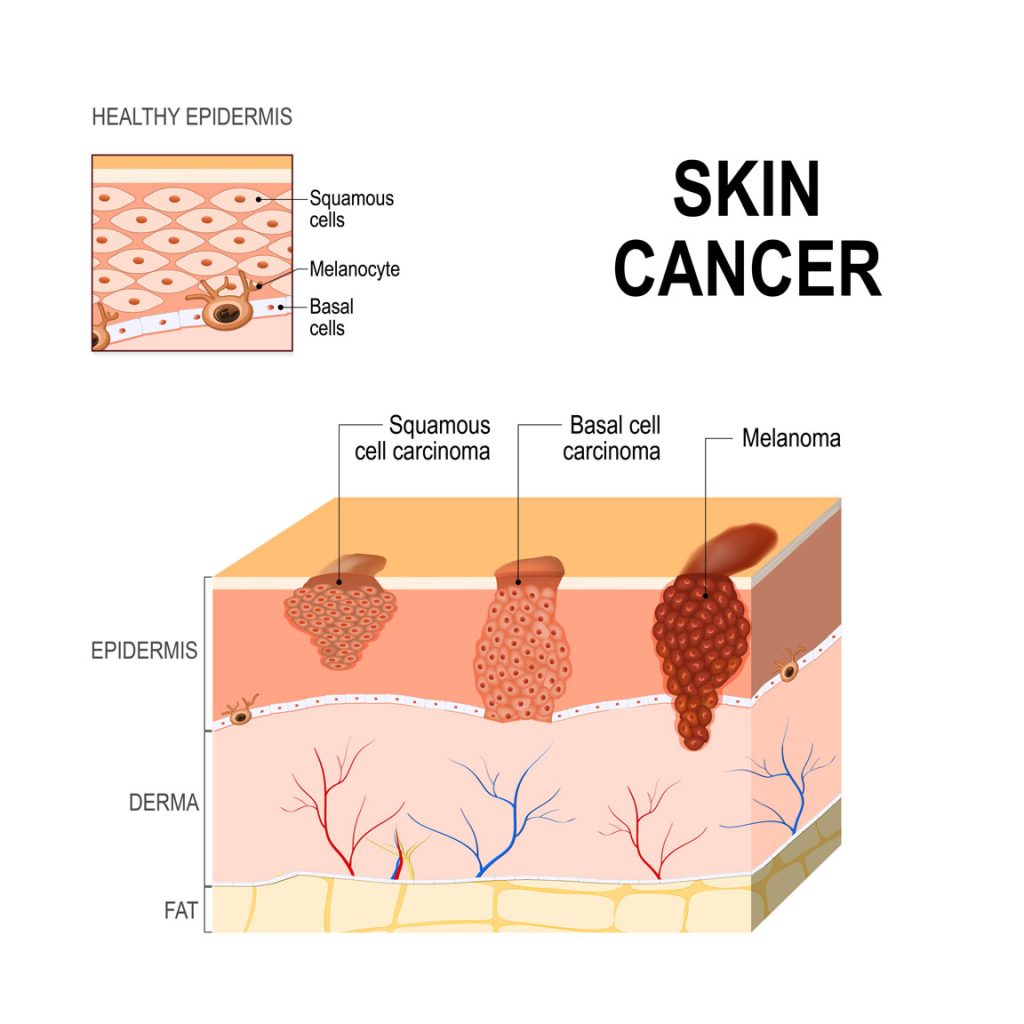
The skin is the body’s largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer) and the dermis (lower or inner layer). Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
Melanoma, the third most common type of skin cancer, begins in the melanocytes. Of all types of skin cancer, melanoma causes the most deaths because of its tendency to spread to other parts of the body, including vital organs.
Most cases of skin cancer are caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, tanning beds, or sunlamps. UV rays can damage skin cells. In the short term, this damage can cause a sunburn. Over time, UV damage adds up, leading to changes in skin texture, premature skin aging, and sometimes skin cancer. UV rays also have been linked to eye conditions such as cataracts.
–CDC

What Can I Do to Reduce My Risk of Skin Cancer?
Most skin cancers are caused by too much exposure to UV rays. UV rays come from the sun, tanning beds, and sunlamps. UV rays can damage skin cells.
To lower your risk of getting skin cancer, you can protect your skin from UV rays from the sun, and avoid artificial sources of UV exposure like tanning beds and sunlamps.
Practice Sun Safety
The UV Index forecasts the strength of UV rays each day. If the UV index is 3 or higher in your area, protect your skin from too much exposure to the sun. CDC recommends several ways to protect your skin when the UV index is 3 or higher:
- Stay in the shade.
- Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs.
- Wear a hat with a wide brim to shade your face, head, ears, and neck.
- Wear sunglasses that wrap around and block both UVA and UVB rays.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher.
The EPA’s UV Index Tool provides the UV Index for your location, enabling you to properly prepare for a day outdoors under the sun.
